We’re intimately familiar with Docker, as folks run thousands of Docker image builds per day using Depot. So, troubleshooting Docker issues has become our bread and butter. In this article, we share some of our favorite Docker tools. These are mostly tools that we use ourselves, but we also include some that we have tried out and are interested in using in the future.
Look through our list to see how you can take advantage of these tools for Docker to speed up your development workflow and make it more powerful and convenient.
Depot’s favorite Docker tools
dive — explore image and layer contents
We already wrote about using dive on our blog a while ago — and we still use it today. dive offers a convenient way to inspect layers inside a Docker image.
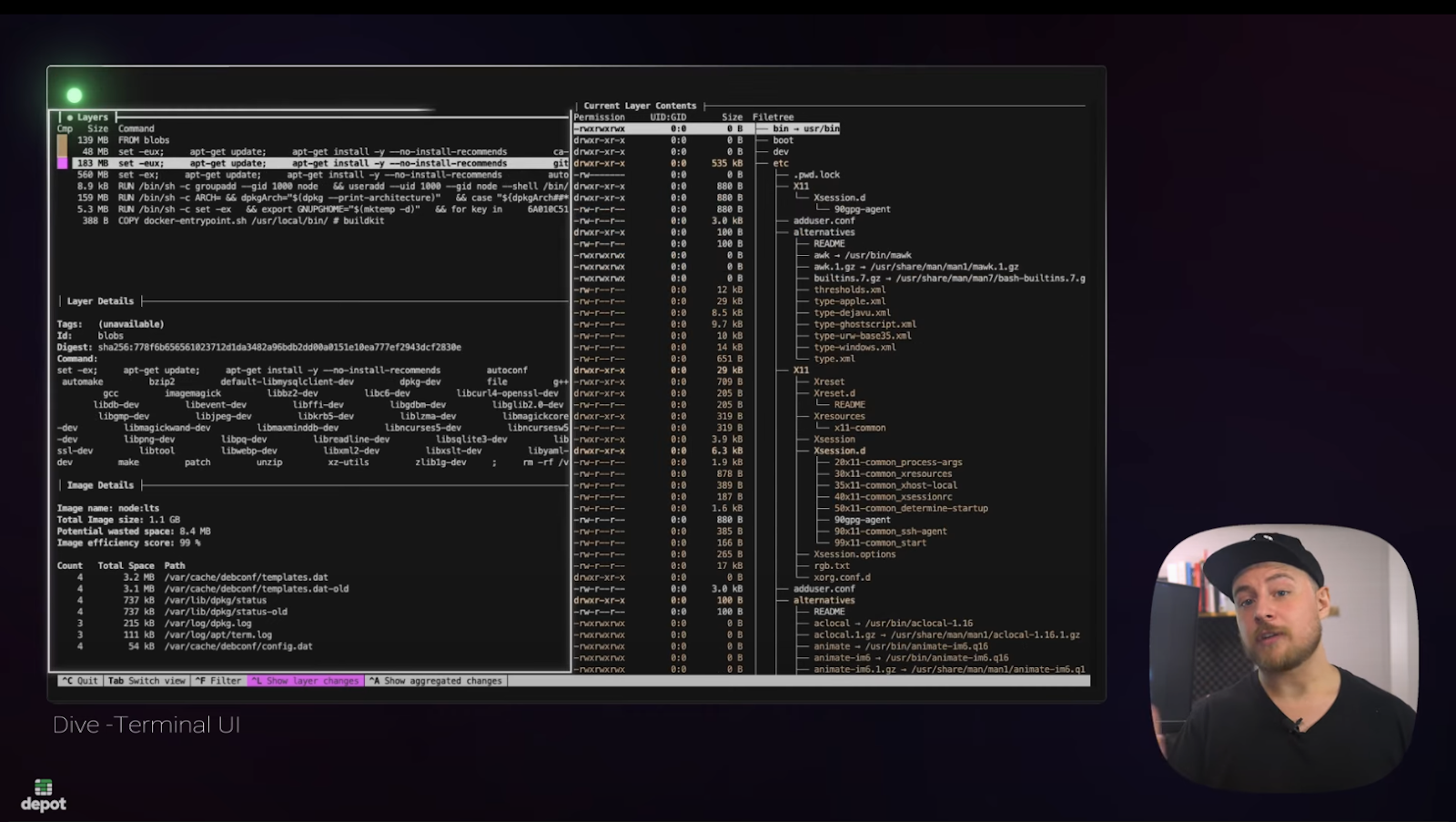
We use dive most often to understand the size of a layer in the image. For example, when an image is bigger than we expect it to be, we fire up dive and try to understand which directories may be storing unnecessary files.
We also find dive useful for seeing file changes from one layer to the next. If the layer is bigger than expected, looking at the steps in the build process that led to the increase in size is the next step in fixing the issue.
Many of the features baked into dive led us to build our Build Insights functionality, which enables you to step through your Docker image build step by step directly from within Depot.
eStargz — build large images with lazy loading
eStargz isn’t a standalone tool but rather an extension of containerd that enables the creation and running of images with lazy loading.
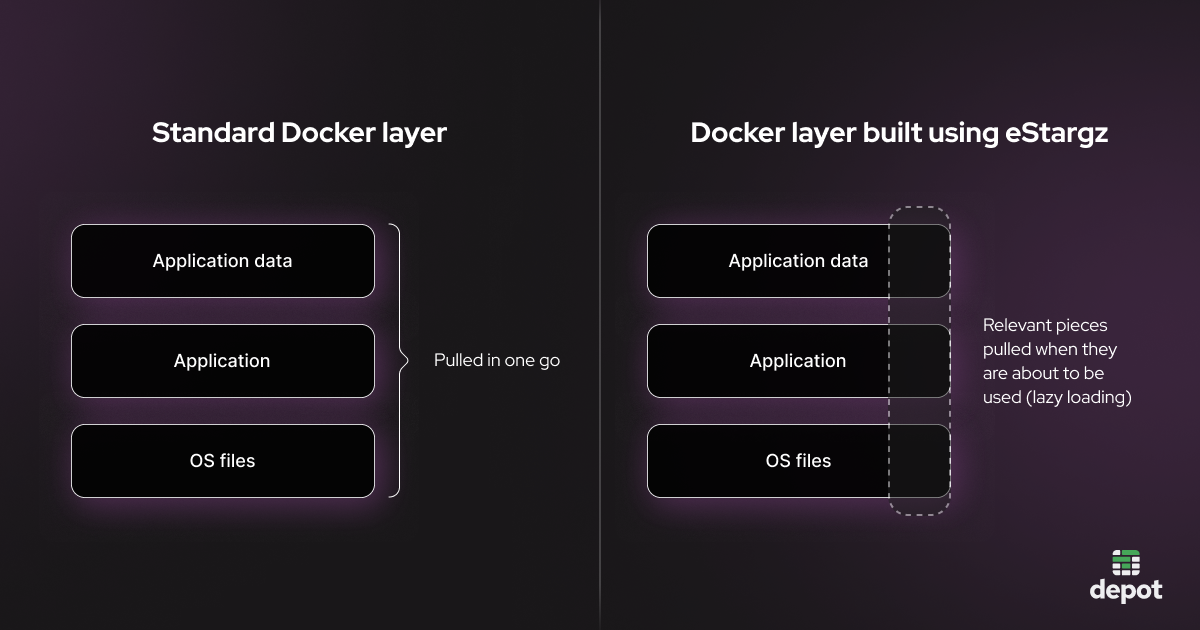
Our use case for eStargz is building very large images that we want to be lazily loaded when they are deployed. This way, we reduce the bandwidth consumed by pulling from the registry (as only the necessary bits are pulled as necessary). The spin-up time for these large containers also goes down since there is no need to wait for the whole image to be downloaded before it can be run.
We actually build all of the images that power our depot.ai project with eStargz enabled so that you can directly copy popular LLM model files into your container images without cloning an entire repo on Hugging Face.
Dev Containers
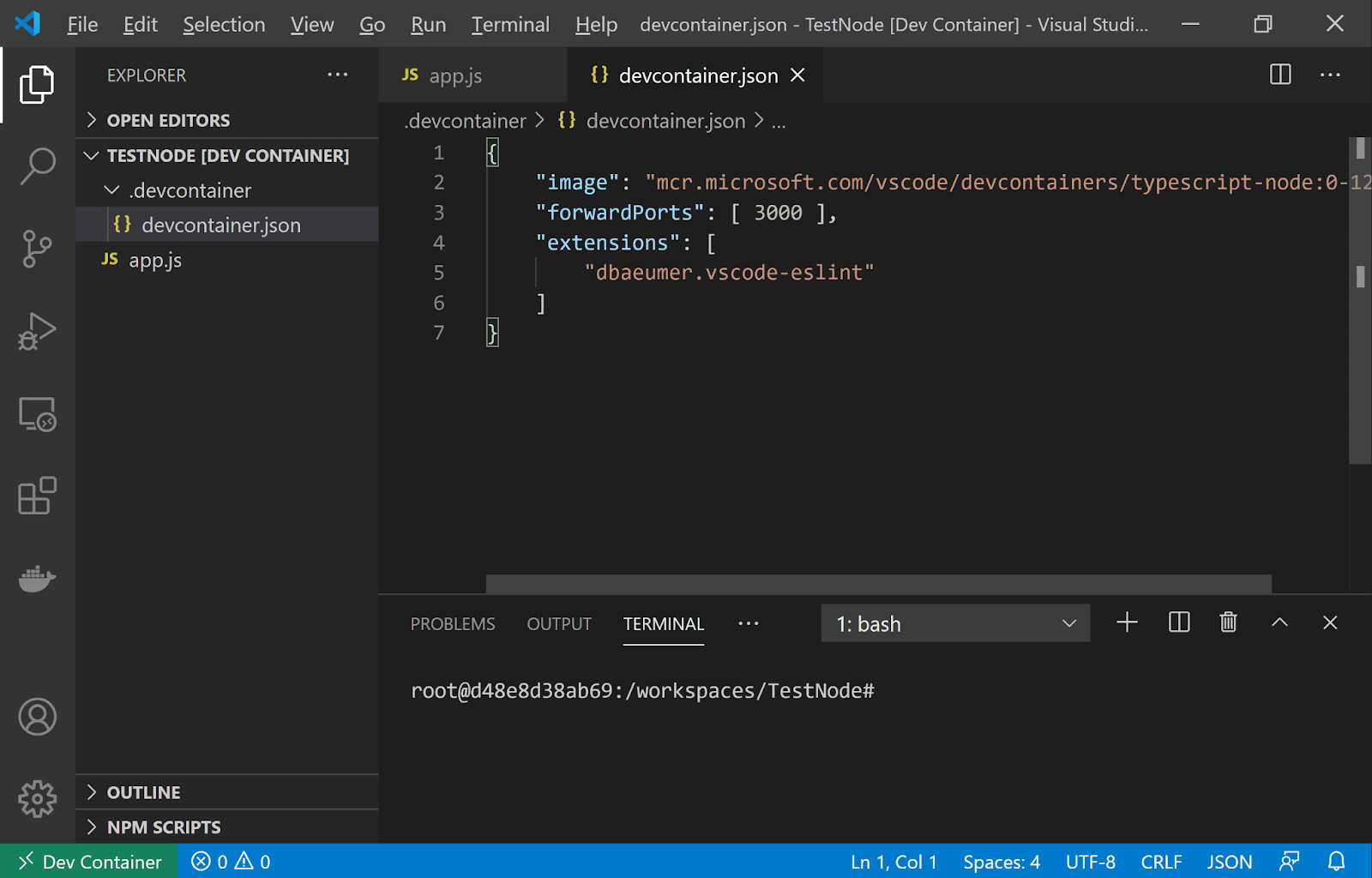
Dev Containers are a way to develop code from within a container with a full IDE inside. To achieve this, the Dev Containers Visual Studio Code extension:
- mounts files from the local filesystem or copies/clones them into the container
- installs extensions inside the container
- runs extensions inside the container with full access to the tools, platform, and filesystem
This means that you can switch your entire development environment just by connecting to a different container.
If you want all of your developers to have the exact same code, environment, and dependencies when they are developing software, Dev Containers can help you achieve that. As an added bonus, you can even use Depot to build your Dev Containers and take advantage of the layer caching and multi-platform builds, check out our Dev Container guide for more information.
hadolint — lint Dockerfiles
hadolint is a linter for Dockerfiles that highlights statements inside a Dockerfile that may be going against the best practices.
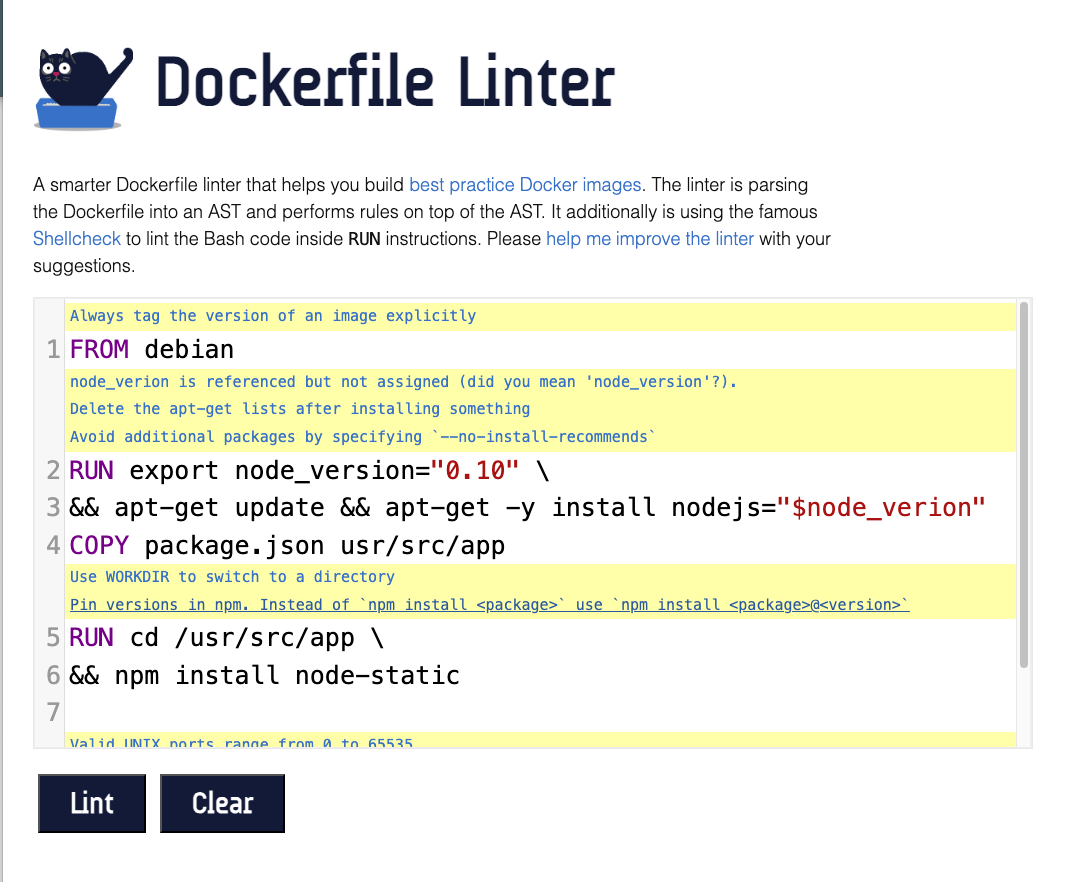
The purpose of hadolint is to warn you about anything that’s against Docker best practices, from formatting and metadata to the use of specific Dockerfile instructions. You can use it locally or implement it as part of your CI process.
We use hadolint and additional Semgrep rules to lint Dockerfiles on every build. You can check out any lint issues with your Dockerfile by clicking into any Docker image build in Depot and selecting the Dockerfile tab.
grype — scan containers for vulnerabilities
grype lets you scan images for security vulnerabilities and create lists of dependencies and OS packages inside container images.
As with many other Docker tools, you can use it both locally during development and in CI. It is quite common to use tools like grype to, for example, fail a CI build if there are any vulnerabilities classified as High or Critical in the packages that the tool finds inside the image, as in the example above.
Dockerfile Explorer — inspect LLB outputs of Dockerfiles
We built the Dockerfile Explorer to make it easier to debug what a Dockerfile is doing at an LLB level.
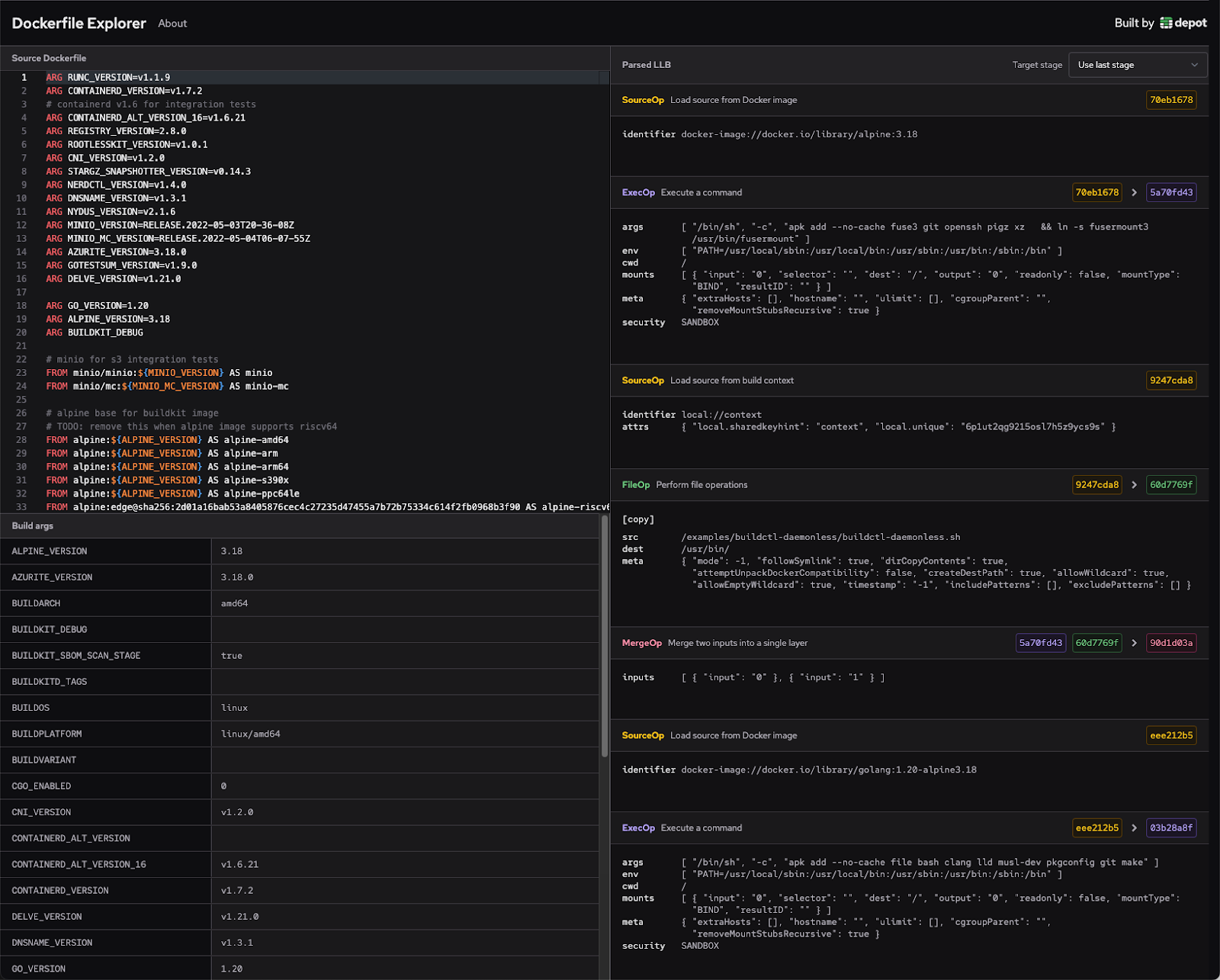
We work a lot with BuildKit, and seeing LLB output frequently helps us understand exactly what BuildKit is doing under the hood.
Sometimes, when we aren’t quite sure how a Dockerfile is being interpreted, we’ll paste it into the interface and see if there is anything unexpected.
Another way we use the Explorer is to paste a Dockerfile, see the LLB output, and then observe how the output changes as we tweak the Dockerfile.
Depot container builds — build Docker containers quickly
We use Depot to build Depot. We build all our production Docker images in Depot, taking advantage of the layer caching and native multi-platform functionality for both Intel and Arm.
Bonus: Some of our favorite Kubernetes tools
We don’t currently use Kubernetes at Depot. But Jacob and I used it a lot in the past before starting Depot, and a lot of folks building container images with Depot are also using Kubernetes.
So, here are a few tools we’ve enjoyed in the past.
K9s — manage Kubernetes clusters through a CLI experience
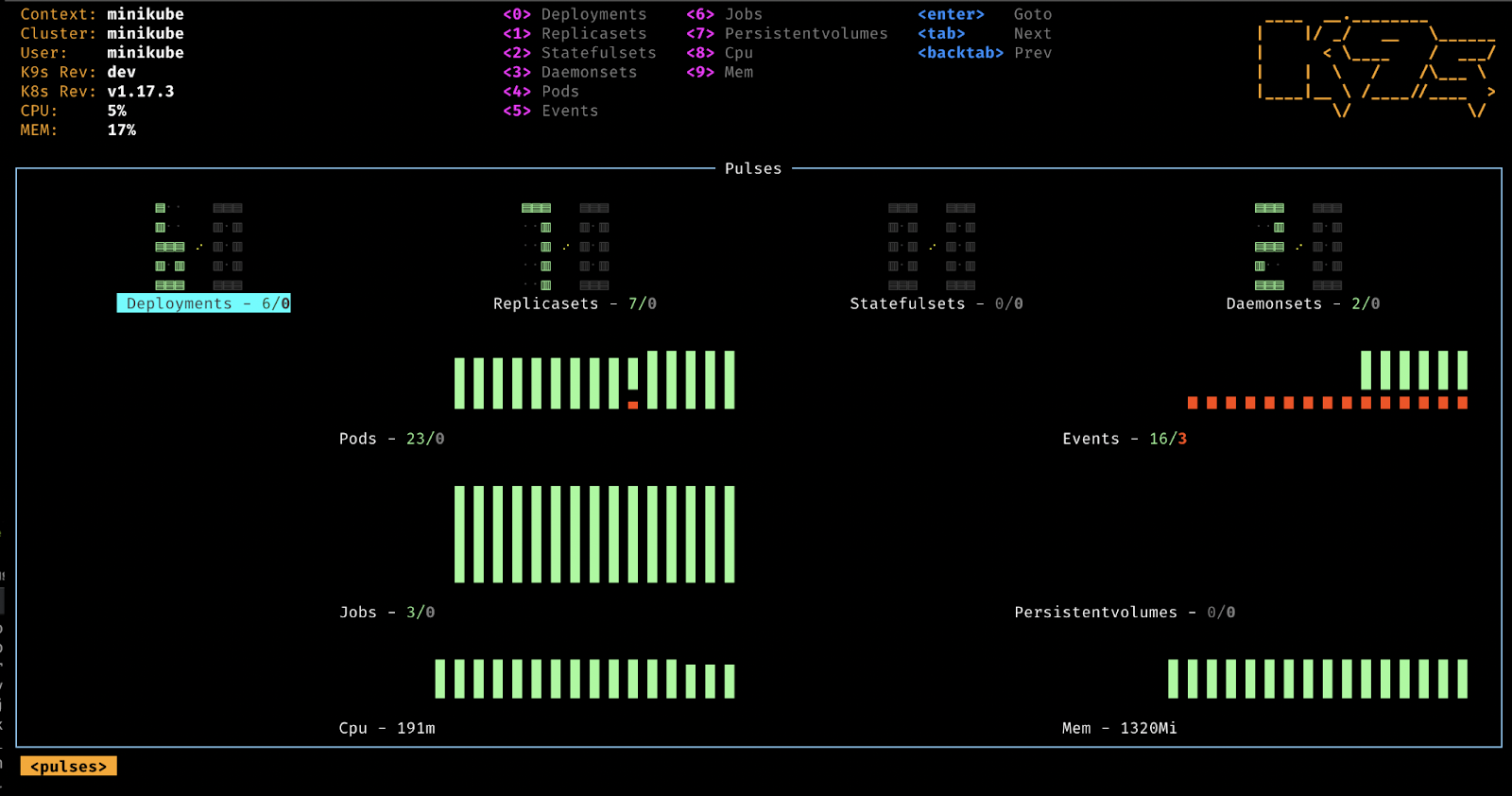
K9s is a convenient way to manage a Kubernetes cluster — or multiple clusters. It’s a terminal UI that is more convenient than the K8s web UI and has tons of useful functionality.
helm — package manager for Kubernetes
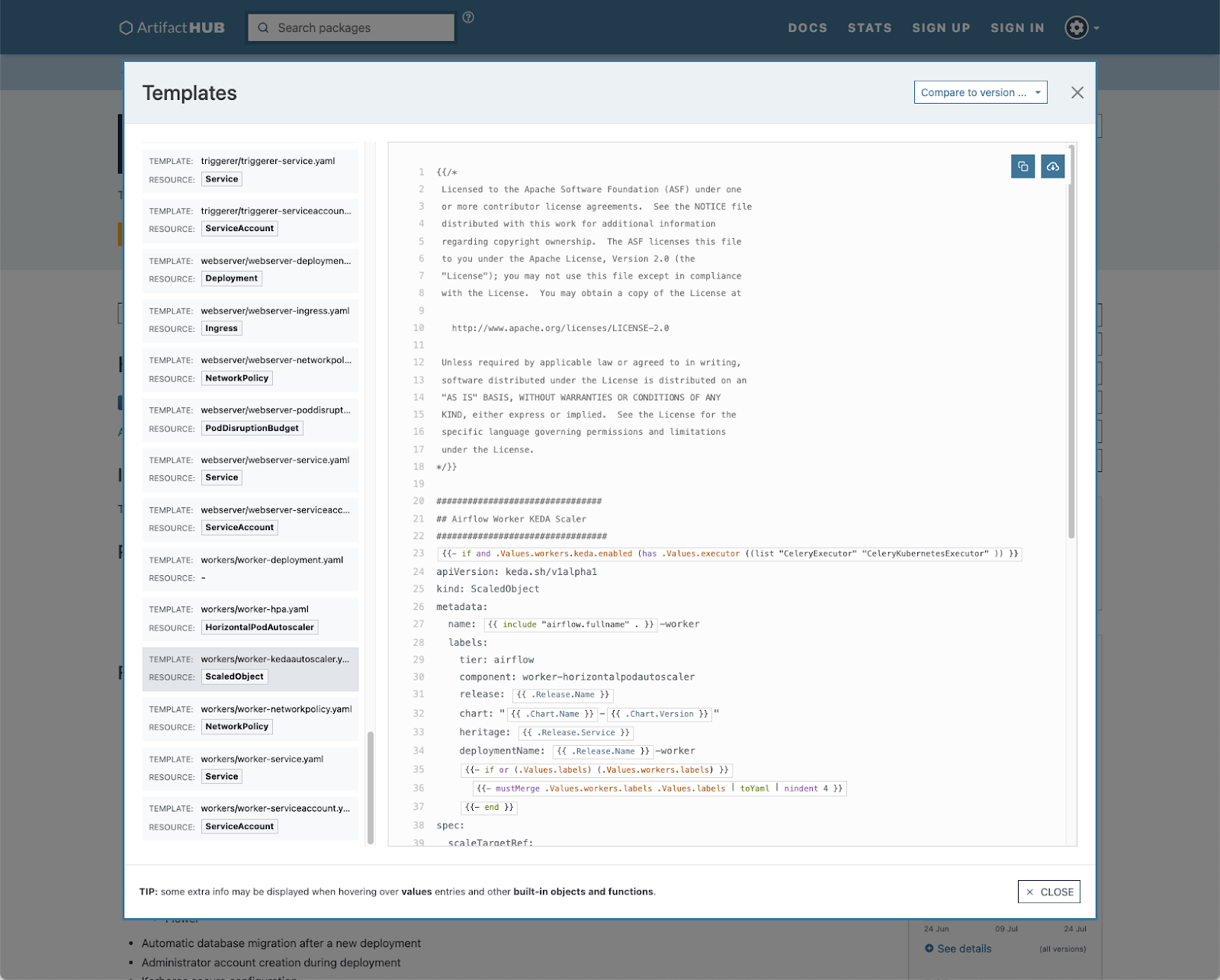
Helm has been useful to us for packaging applications consisting of multiple containers and sets of settings into Kubernetes “packages.” Helm Charts combine config and templates into one bundle that you can edit and then deploy directly to a Kubernetes cluster. You can create your own charts for your own applications, and there is a repository of Helm charts for popular open-source projects.
Summary
In this article, we’ve shared the Docker tools that we like and use.
By taking advantage of the tools in the container ecosystem, you can make your workflow smoother, more helpful, and less time-consuming.
If you work with Docker, we definitely recommend taking note of the parts of the flow that might feel slow or inconvenient to you and investigating tools out there that may solve this. Chances are, there is a Docker tool for that.
Related posts

